Gate valves are essential shut-off devices in industrial piping systems. Their reliability and lifespan are directly related to the safety and stability of the entire system. They can be categorized into various types based on their structure (such as gate disc design and stem movement), and their daily maintenance priorities vary. WEIZIDOM, based on years of industry experience, has summarized the following key maintenance points for different types of gate valves.
Parallel gate valves have two parallel plates, which rely on medium pressure to achieve a seal. During routine maintenance, focus on checking for gate sticking and wear on the sealing surfaces. Regular cleaning of the gate disc groove is recommended to prevent impurity accumulation that may affect the sealing effect. For double-disc gate valves, check for failure of the intermediate spring.
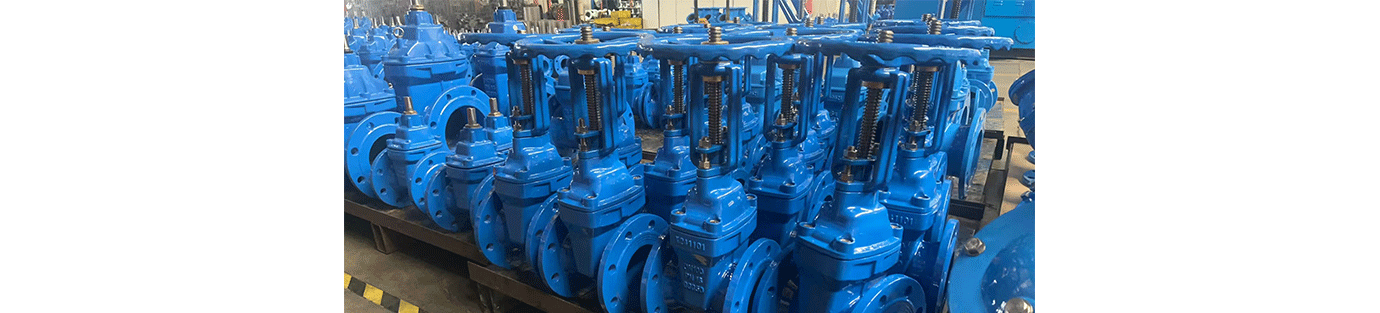
Wedge-type gate valves achieve sealing through the wedge-shaped action between the gate disc and the valve seat. During maintenance, pay special attention to wear on the sealing surfaces and regularly check for changes in the wedge angle. Single-disc wedge valves require attention to potential seizures caused by thermal deformation; double-disc gate valves require checking the flexibility of the hinge mechanism.
The stem of a rising-stem gate valve rises and falls with opening and closing operations, making it easy to visually determine the valve’s status. Maintenance focuses on cleaning and lubricating the stem threads. Regularly remove thread buildup and apply high-temperature grease. Also, inspect the stem surface for pitting or scratches, as these damage can compromise the packing seal.
The stem of a non-rising-stem gate valve rotates but does not rise or fall. Its height dimension is small, but the opening cannot be visually determined. During routine maintenance, pay special attention to the wear of the stem nut, which is the most vulnerable component of non-rising-stem gate valves. Torque changes can also be used to determine the internal gate’s operating status. Abnormal torque increases may indicate gate sticking or damage to the sealing surface.
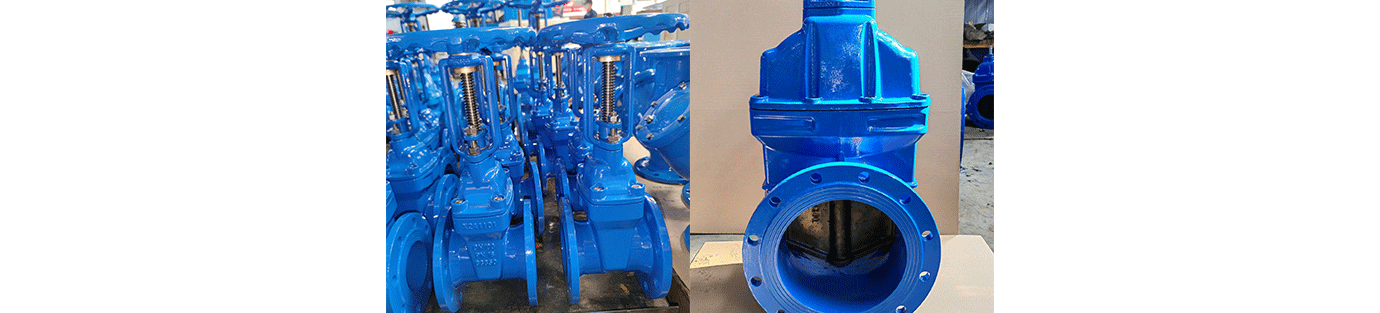
Manual gate valves have a simple structure, so maintenance focuses on lubrication and checking the flexibility of the transmission mechanism. Regularly lubricate transmission components such as gears and handwheels, and check the handwheel for looseness and ease of operation. For large-diameter valves, carefully inspect the bypass valve for leaks.
Electric gate valves require attention to both the valve body and the electric actuator. The valve should be inspected for reliable connection to the actuator. Electric actuators should regularly check parameters such as motor insulation, limit switch accuracy, and torque protection settings. The gearbox should be kept properly lubricated and the actuator should be cleared of moisture.
For pneumatic and hydraulic gate valves, maintenance should focus on the drive cylinder and control system. Regularly check the seals of the drive cylinder to prevent media leakage. Keep the air supply or hydraulic oil clean and filter it regularly. Check the sensitivity of control components such as the solenoid valve and positioner.
Metal-sealed gate valves are resistant to high temperatures but have relatively poor sealing properties. During maintenance, focus on checking the seal surface for wear. Minor wear can be repaired by grinding, while severe wear requires seal replacement. Under high-temperature conditions, pay attention to changes in seal surface stress caused by thermal expansion.
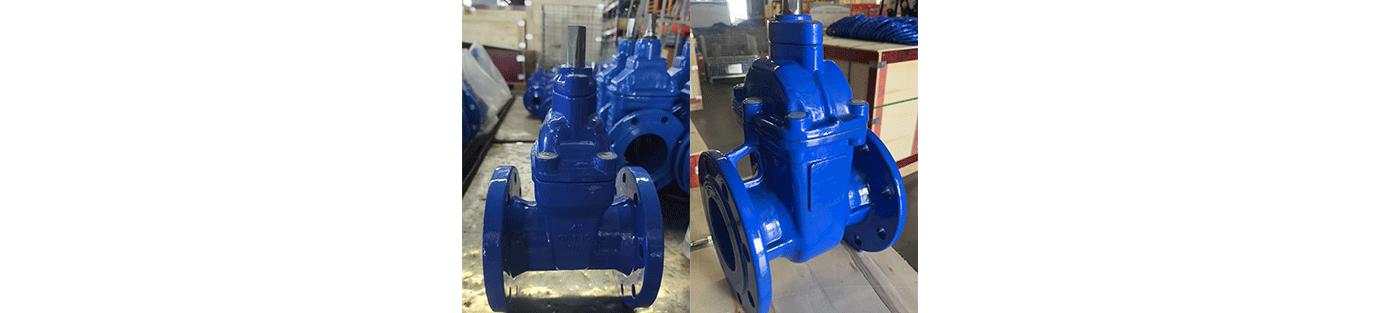
Soft-sealed gate valves, made of non-metallic materials such as rubber and polytetrafluoroethylene, offer excellent sealing properties but are not resistant to high temperatures. During routine maintenance, check the soft seals for aging, deformation, or damage, and replace the sealing material regularly. Avoid sharp particles in the media that could damage the soft seal surface.
The packing seal is a key component in preventing valve stem leakage. Regularly check the packing gland for looseness and whether the packing needs to be replenished or replaced. When adding new packing, ensure the cuts are staggered and the tightening force is appropriate to ensure a tight seal without obstructing the valve stem.
Q: What daily inspections and maintenance should be performed on gate valves?
A: Gate valves should be visually inspected, the stuffing box inspected, cleaned, lubricated, and regularly maintained to prevent leaks and seizures.
Q: What considerations should be taken when selecting replacement parts (such as packing and gaskets)?
A: When replacing parts, first ensure that the material is compatible with the media, temperature, and pressure. For example, graphite should be selected for high temperatures, and PTFE for corrosive media.
Q: When should a gate valve be replaced rather than repaired?
A: If the valve body is cracked, severely corroded, leaking repeatedly, or the repair cost is prohibitive (50%-60% higher than a new valve), especially when handling high-risk media, replacement is recommended rather than repair.